

On-Page SEO is perhaps the most critical part of improving your site’s search traffic. Over the past few years, Google has released several algorithm updates (Penguin, Panda, and Hummingbird).
Due to these updates, SEO experts all around the world have had to modify their on-page SEO tactics to reclaim their former search engine rankings.
To help you keep up to speed with the ever-changing SEO landscape, we’ve compiled a list of 20 on-page SEO tips.
Our focus in this article will be to show you the most actionable SEO tactics that will improve your search rankings, boost your traffic, and enhance the user experience on your website.
But first, let’s cover the basics…
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing web pages to help them rank better in search engine result pages (SERPs).
Moz explains it best:
On-page refers to both the content and HTML source code of a page that can be optimized, as opposed to off-page SEO which refers to links and other external signals.
Contrary to popular belief, on-page SEO is more than just optimizing the meta tags on your website. It’s a much more complex topic that’s evolved a lot over the years. As a result, it’s important to keep pace with the latest SEO best practices.
Pro Tip: To perform an on-page SEO audit for your website, you can use Free SEO Checker by Sitechecker.
Here are 20 actionable tips to optimize your on-page SEO.
20 Actionable On-Page SEO Tips
1. Update or Delete Older Blog Posts
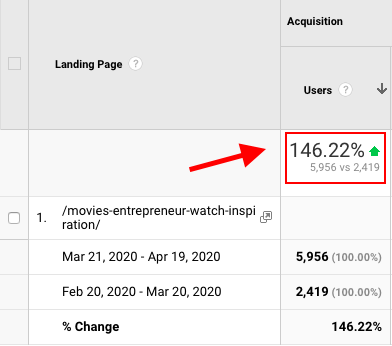
Want to know how I increased organic traffic to one of my old blog posts by 146% in 30 days? I updated it with new information and relaunched it.

You can do the same with a few of your posts.
That said, you should prioritize certain blog posts over others. You have a much better chance of improving the ranking of a blog post that ranks at positions #5 – #10 on Google than a post that ranks at position #30.
The post that I updated in the above example was ranking at position #5 for the keywords “best movies for entrepreneurs.” After the update, it soon started ranking consistently at position #1, and hence the traffic boost.
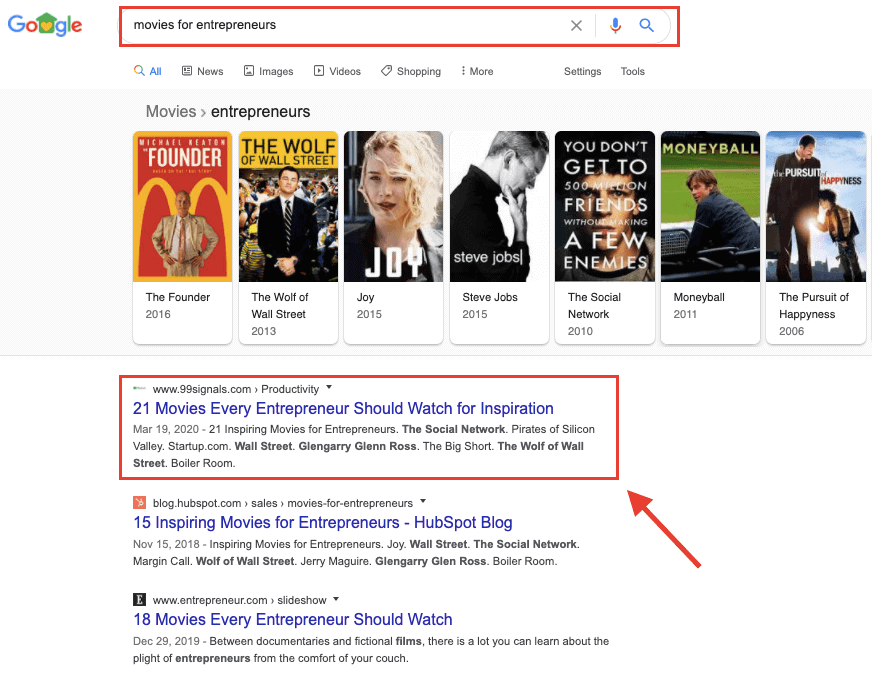

That’s not to say that the blog posts that don’t rank high on Google don’t deserve an update. They certainly do. It’s just that you need to first update and refresh the content on posts that are already ranking high in SERPs, and then move on to other posts.
To find pages that need an update on your site, you can dig into your Google Analytics to identify pages that are losing traffic.
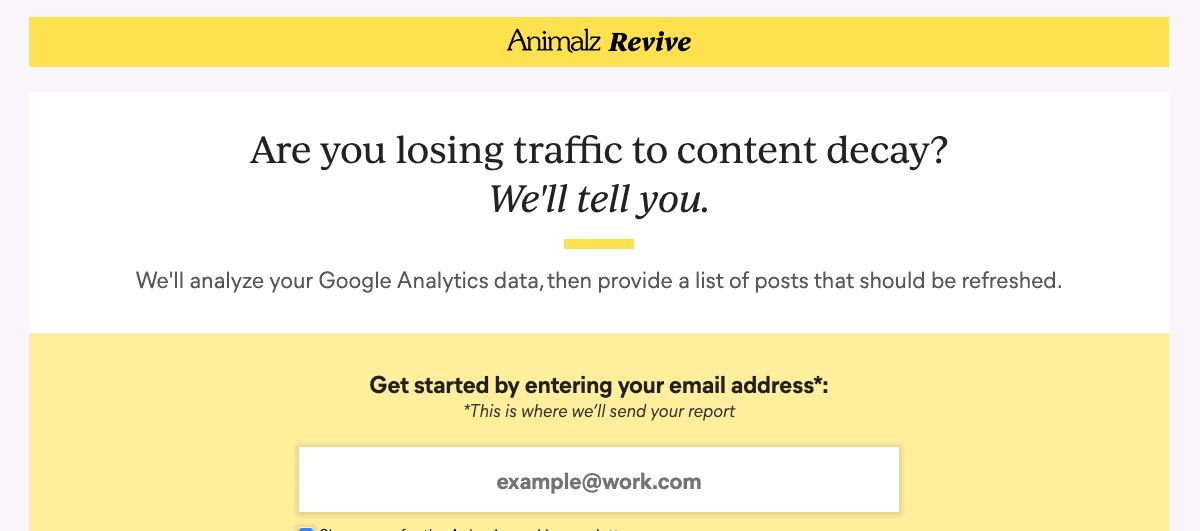
You can also use a free tool like Animalz Revive which automatically syncs with your Google Analytics to find pages with the biggest percentage drop in traffic.

Updating and relaunching your old posts is a guaranteed way to breathe new life into your content. But not all posts deserve a revival.
Deleting posts may seem like a pretty controversial tip, but this trend of deleting older, irrelevant posts seems to be catching on.
SEO experts such as Brian Dean of Backlinko and Rand Fishkin of Moz recommend that you delete older, mediocre posts that aren’t bringing you much search traffic. Oftentimes these posts are short and sweet 100-400 word blog posts that lose out to 2,000-5,000-word articles that are detailed and informative.
The truth is if your old posts aren’t bringing any organic traffic, they are pretty useless. So delete or “noindex” them.
Recommended reading: Content Upgrade Strategy: How to Optimize Old Blog Posts to Get More Traffic
2. Align Your Content with Search Intent
Search intent is the goal behind every search query. Satisfying search intent is Google’s top-most priority.
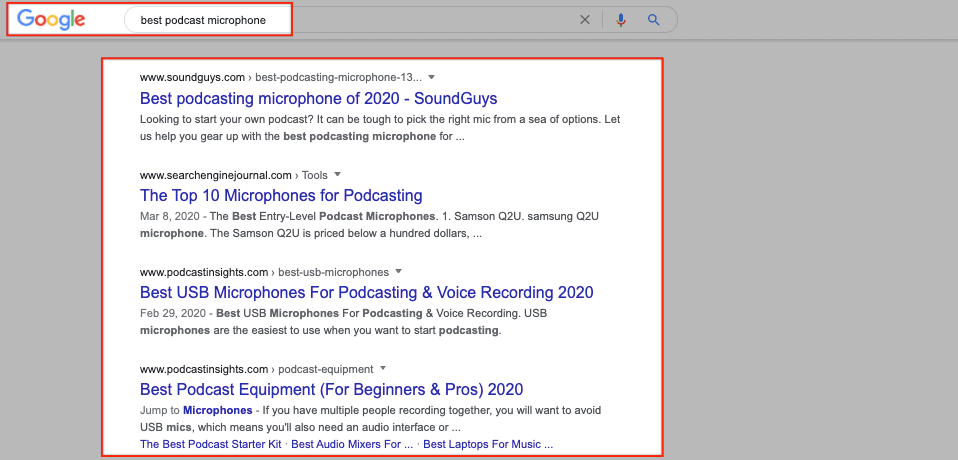
For instance, when someone searches for “best podcast microphone,” Google knows that the user intent here is not to buy, but to learn. The user is looking for expert advice or guidance on the best podcast microphone on the market.
As a result, the search results that dominate page 1 for this query are mostly list posts.

On the other hand, when someones searches for “buy audio technica at2020 online,” Google understands that the user intends to buy the specific microphone and wants to buy it online. Hence, the SERPs on page 1 are mostly eCommerce and product pages.
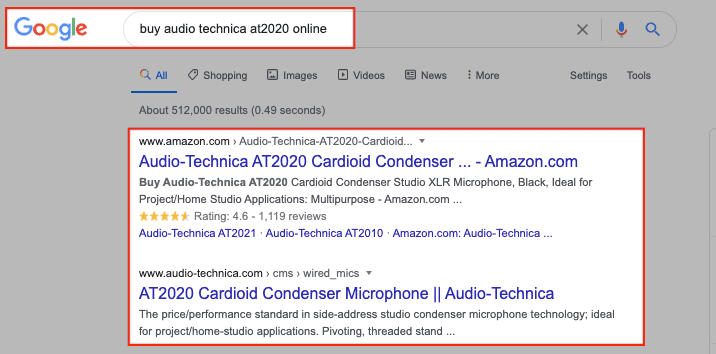

Long story short, if you’d like your pages to rank higher on Google, you need to make sure your content matches the search intent of your target keywords.
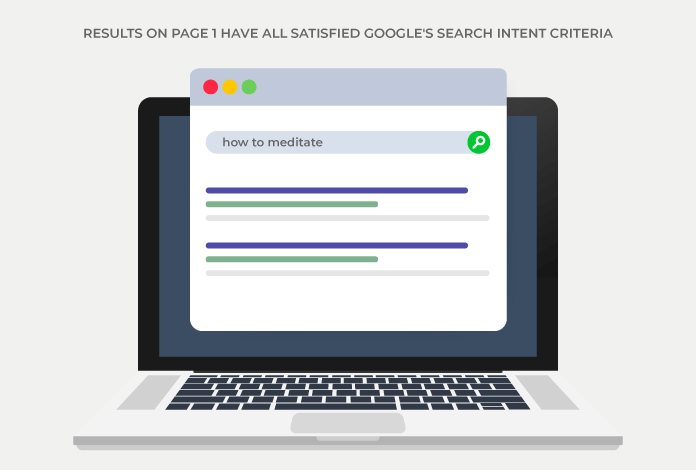

Before you start creating content for your target keyword terms, it’s important that you understand the search intent behind the keywords.
Most searches fall under one of these four search intent types: informational, navigational, commercial, and transactional.


Once you’ve identified the search intent of your target keywords, the next logical step would be to select the right content type. The four content types that dominate SERPs are as follows:
- Blog posts
- eCommerce category pages
- Product pages
- Landing pages
Based on the search intent of your target keywords, select the content type that is most likely to rank high for those keywords. Check out the existing organic competitors for your target keywords and aim at creating unique content to stand out amidst competition.
To learn more about optimizing your content for search intent, check out Search Intent and SEO: The Ultimate Guide.
A canonical URL (an HTML link tag with attribute rel=canonical) allows you to tell search engines that certain similar URLs are actually one and the same.
Sometimes you may have similar content accessible under multiple URLs or websites. This is especially the case with eCommerce websites. By adding a canonical tag, you can ensure that similar content exists on multiple URLs without affecting your search rankings.
Let’s say you have an online furniture store selling coffee tables. You may have multiple URLs on your website with similar information on coffee tables. This can cause duplicate content issues and hurt your search rankings.
This problem can be easily fixed by using canonical tags. You can use your preferred page as the canonical URL (https://www.furnitureonline.com/coffee-tables) and add a canonical tag to similar pages (for instance, https://www.furnitureonline.com/coffee-table-with-storage). This will help Google index only the preferred page while ignoring the rest.
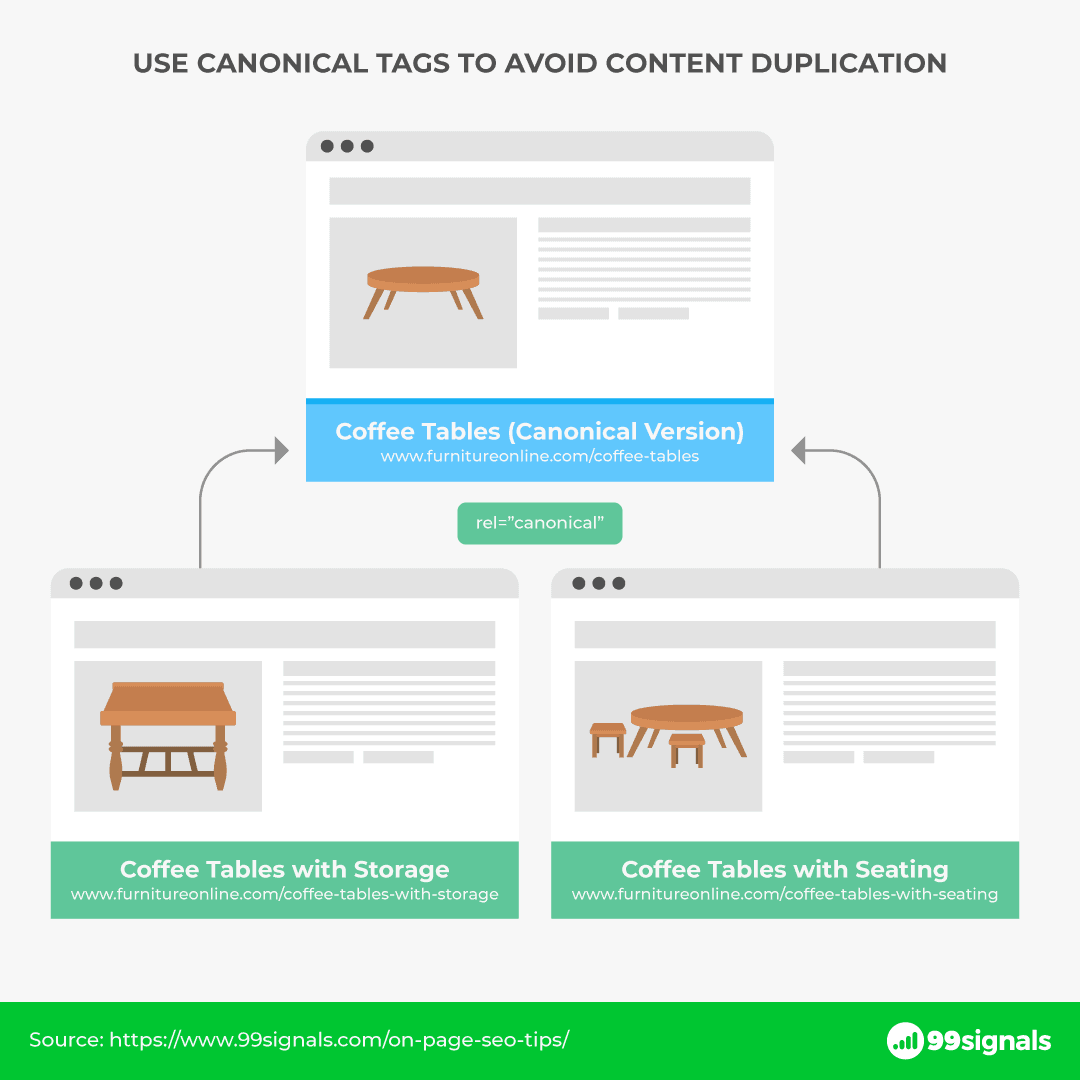

Canonical tags are not just useful for eCommerce websites.
Some of my posts at 99signals are repurposed or syndicated on my agency blog because we essentially cover the same topics. Using a canonical URL helps me avoid duplicate content issues which can really hurt the site’s SEO.
If you use an SEO WordPress plugin like Yoast or All in One SEO Pack, it’s easy to use the canonical tag. On Yoast, just click on the Advanced tab, and type the URL in the Canonical URL box.
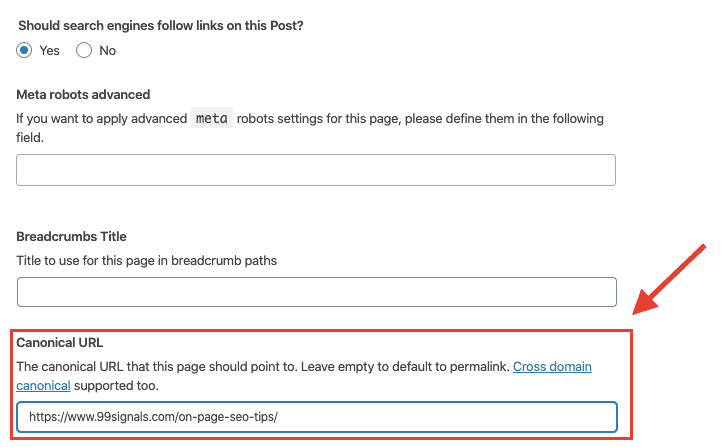

Related: 19 Best SEO Plugins for WordPress
4. Add LSI Keywords to Your Content
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords are “synonyms and closely-related terms.” Google uses LSI keywords to evaluate a page’s relevancy and quality.
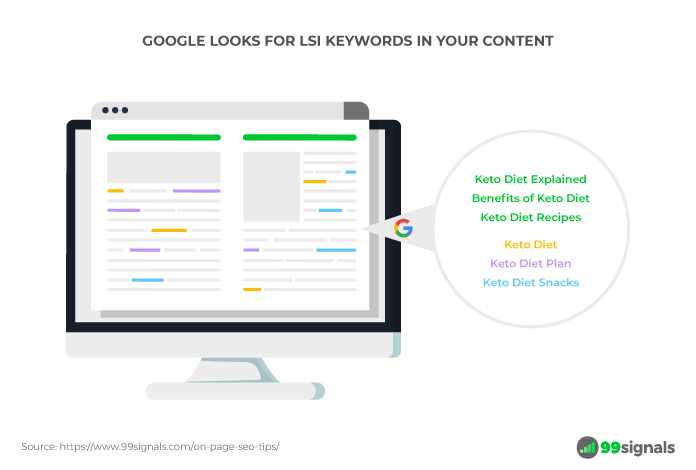

In other words, when you include LSI keywords in your content, you help search engines determine what your page is all about.
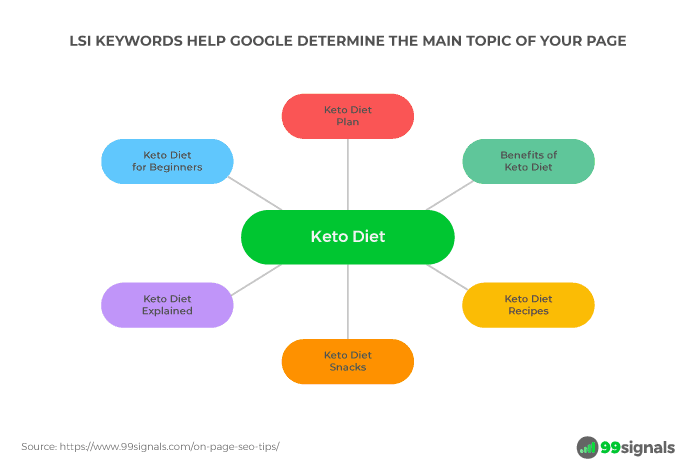

How do you find these LSI keywords?
Just give a Google search and scroll down to the bottom of the page to see other searches related to your search query.
So if you’re writing an article on “SEO Tips,” the LSI keywords you should include in your content are “unique SEO tips” and “advanced SEO tips” as you can see below.


If you’re a Semrush user like me, you can find even better LSI keywords by following these steps:
- Type your keywords in the Semrush search bar
- Scroll down to see “Phrase Match Keywords” and “Related Keywords” for your search terms
- Pick a couple of keywords from each category and include them in your content
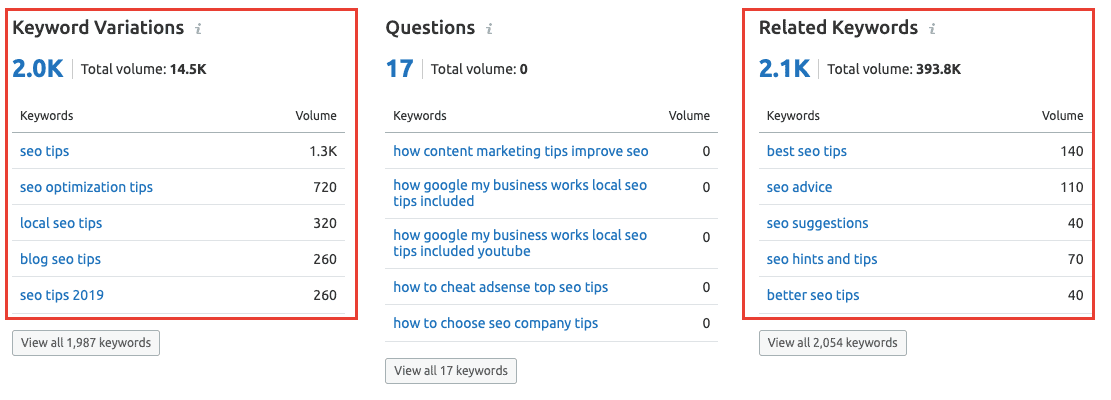

You can do this for free by signing up for a 30-day free trial of Semrush.
You can also use LSIGraph, a free tool, which helps you discover LSI keywords that are just right for your topic and niche.
5. Increase CTR with Schema Markup
Schema markup is SEO’s latest evolution, but it’s rarely used despite being a powerful Google ranking signal.
According to Searchmetrics, only 0.3 of all websites use schema markup. This means that there are a ton of websites missing out on boosting their SEO score.
But what exactly is a schema markup?
Schema markup is a code that you put on your website to help search engines return more informative results for users. In other words, schema markups can offer rich snippets in Google’s search results which in turn can boost your SEO as well as your CTR.
Schema markup helps your site rank better in SERPs for all types of content, including:
- Articles
- Local businesses
- Restaurants
- TV episodes and ratings
- Book Reviews
- Movies
- Software Applications
- Events
- Products
Here’s an example of movie review sites that have schema markups:


6. Use Short, Keyword-Rich URLs
Google and other search engines prefer shorter URLs over longer ones. Shorter URLs are also good from user experience perspective.
It’s also a pretty good idea to include your focus keywords in the URL.
This is because:
- Keywords in the URL give an indication to users who see your URL on social media, in an email, etc. and get a fair idea of what kind of content they can expect by clicking on it.
- URLs get copied and pasted regularly. When there’s no anchor text used in a link, the URL itself serves as that anchor text (yet another powerful ranking signal).
- Keywords in the URL show up in search results. According to research, URL is one of the most prominent elements users consider when selecting which site to click.
So avoid ugly URLs that look like this:
99signals.com/27-09-2016/category/article-titile
…and opt for keyword-rich, short URLs like this:
99signals.com/article-title
7. Publish Long-Form Content
There are many definitions of what long-form content truly means. While some say it’s articles with 700 words or more, others argue that long-form articles are longer with over 2,000 words. However, there is some consensus among marketers that long-form content refers to articles of around 2,000 words or longer.
This step-by-step SEO guide by Neil Patel is a good example of long-form content.
Google SERPs are dominated by these long-form articles which are detailed, informative, and cover a particular topic in-depth.
SEO experts believe there is a strong correlation between long content and higher rankings.
Check out this graphic from Backlinko which illustrates the correlation between Google SERP position and long-form content.
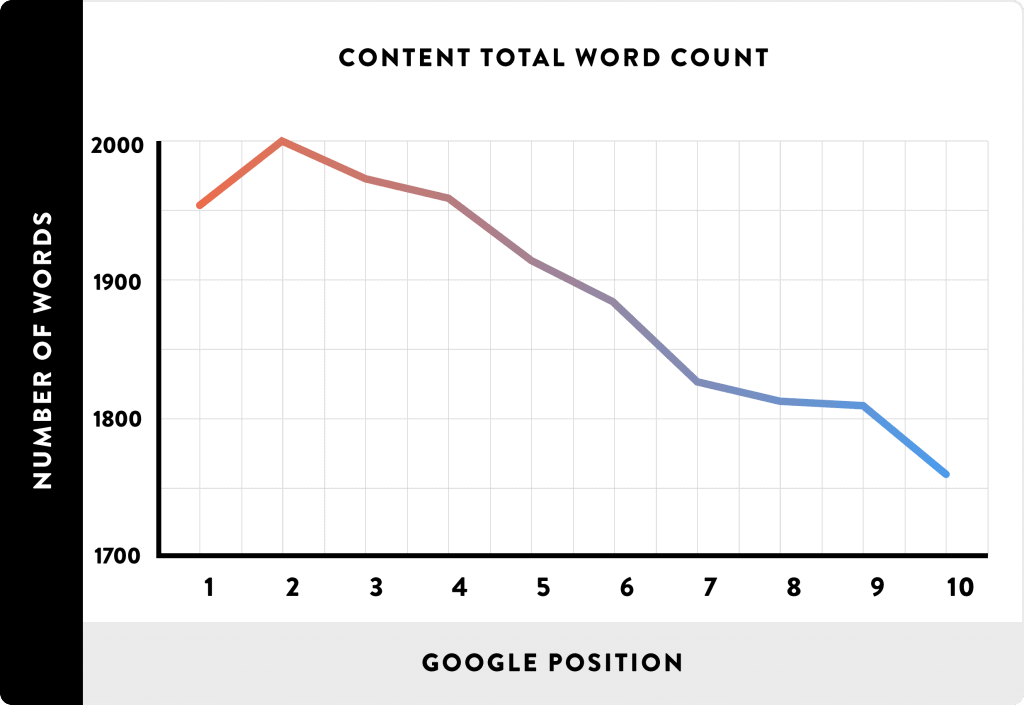

Image Credit: Backlinko
And this graph from a study conducted by serpIQ:
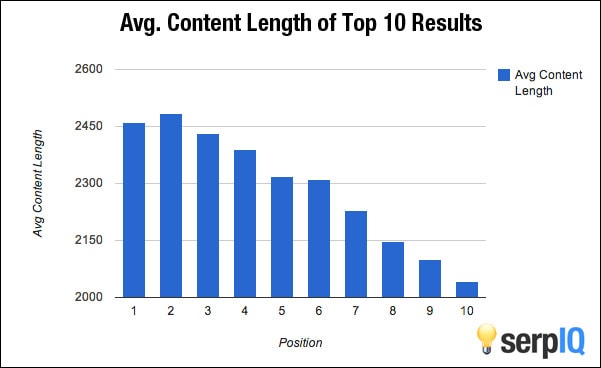

As you can see, articles with 2,000-2,500 words are currently dominating SERPs.
Short and sweet 300-500 word blog posts are dead. If you want to rank higher in search results, publish long-form content.
Related: [Answered] How Long Should a Blog Post Be?
8. Write Compelling Headlines
Here’s the harsh truth: It doesn’t matter how well-researched or in-depth your article is. If it’s not accompanied by a compelling headline, it will be ignored by your target audience.
Which is why you need to put some effort into crafting attention-grabbing headlines that resonate with your audience.
Backlinko conducted a CTR study in which they found emotional headlines got clicked on 7% more often than headlines that didn’t have an emotional sentiment.
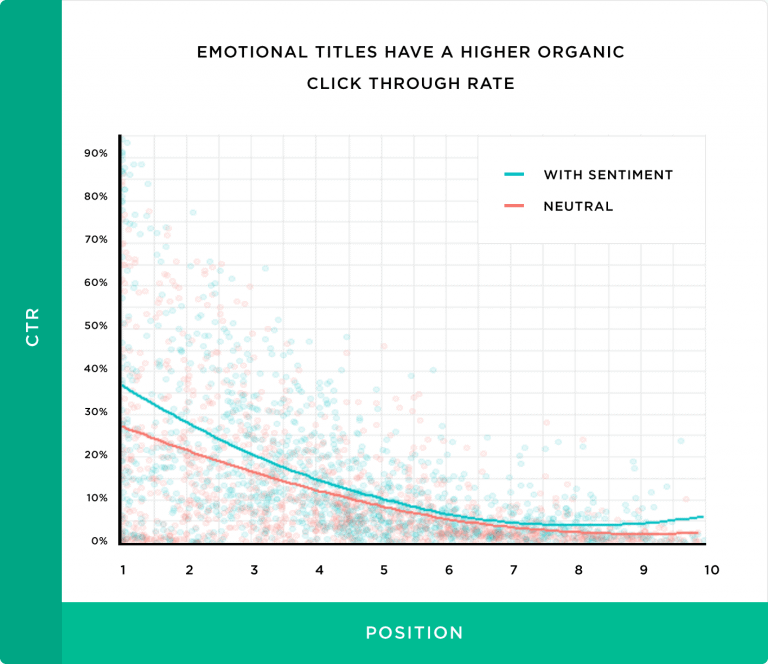

Image Credit: Backlinko
To add an emotional punch to your headlines, make use of power words. Here’s a list of 401+ useful power words you can choose from.
If you need help crafting the perfect headline for your post, you can use a free tool like CoSchedule’s Headline Analyzer to test the quality of your headline.


Headline Analyzer will analyze your headline and provide you with a headline score by studying the overall structure, grammar, and readability of your headline. It will also show recommendations on how to improve your headline to help it perform better in SERPs.
9. Improve Your Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are often overlooked because they don’t have a direct impact on search rankings. That may be true, but meta descriptions can increase the click-through rate (CTR) which in turn can significantly improve your rankings.
Backlinko’s CTR study found that pages with meta description get 5.8% more clicks than pages without a description.
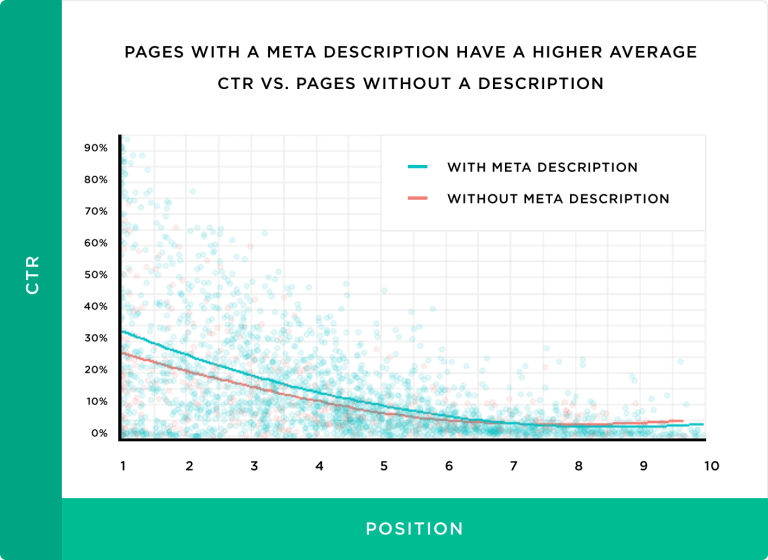

Image Credit: Backlinko
An SEO best practice is to write unique meta descriptions for your posts, homepage, product pages, categories, and any other important page on your site.
10. Optimize Your Page Speed
If you want your visitors to have a seamless experience on your website, you need to improve your page speed. Page speed is also one of signals used by Google’s algorithm to rank pages. As such, you need to constantly monitor your page speed using tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix.
Here are some of the ways you can improve your page speed:
- Enable browser caching
- Minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML files
- Reduce server response time
- Reduce redirects
- Optimize images – See #11 for more details
- Use a Content Delivery System (CDN)
11. Optimize Your Images
Strategically-placed images within your content provide a much-need visual break from the text. That said, you need to make sure the images on your site are optimized to drive more organic traffic.
The first thing you need to do with your images is compress them. Large image file sizes impact page speed. As such, you need to compress the file size of your images before you upload them to your site.
Image compression tools such as TinyPNG or ImageOptim (if you’re a Mac user) can help compress your images without compromising their quality.
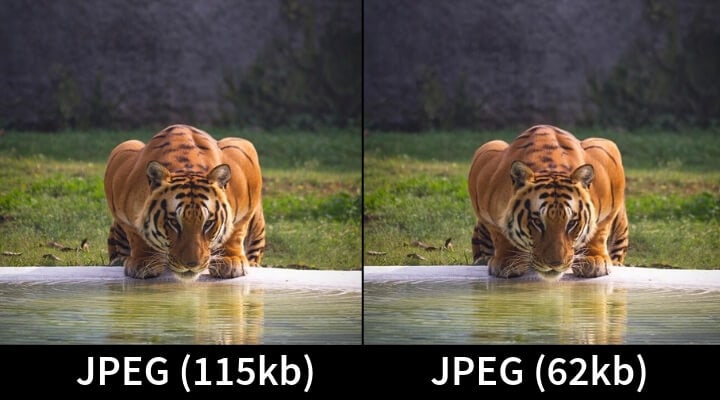


In addition to image compression, here are some other ways you can optimize your images:
- Include descriptive filenames for your images – Despite advancements in Google’s machine learning capabilities, you need to include a descriptive filename for your images to help Google better understand your images.
- Provide alt text for images – Google and other search engines can’t see what’s in an image. Instead, they use the image filename and alt-text to understand what’s in an image. That’s why you should include your target keywords in your image alt-text.
- Select the best file format – JPEG and PNG are two of the most common image formats on the Internet. Though JPEGs have a smaller file size, they are not best option when you have text in your images. In such cases, opt for PNG. For everything else, go with JPEG.
- Lazy-load your images – When you lazy-load non-critical resources like images and videos, you essentially load them only when your visitors need them. Lazy-loading can boost your site speed. If you’re a WordPress user, install the free a3 Lazy Load plugin to activate lazy-loading on your site.
- Resize your images – Resize your images in line with your site dimensions to further improve your site’s performance. Use the free SmartResize tool to resize your images in bulk.
For more insights on each of the above tips, check out Image SEO: 7 Actionable Tips to Supercharge Your Organic Traffic.
12. Put Your Keyword Early In Your Title Tag
Title tags show up in the SERPs as the clickable headline for a given search result. We’ve already established the importance of writing a compelling headline that resonates with your target audience.
According to Moz’s testing and experience, keywords that are placed at the beginning of your title tag may have more impact on search rankings.
So when it makes sense, put your focus keywords at the beginning of your content’s title tag. But don’t go overboard and stuff your title tag with repeat variations of the same keyword.
Sometimes using a keyword too often can be detrimental to your site’s SEO. This is especially true if you repeat the keywords over and over in your H1, H2, H3 tags.
So in order to avoid keyword stuffing, use keyword variations of your target keywords in H1 and H2 tags.
14. Leverage Internal Linking
Internal linking helps reduce your site’s bounce rate and makes the user stay engaged in your site longer. In addition to this, it can also provide a slight boost to your organic traffic.
Here’s a simple trick: Link from top-ranking pages on your site to pages that you’d like to rank for.
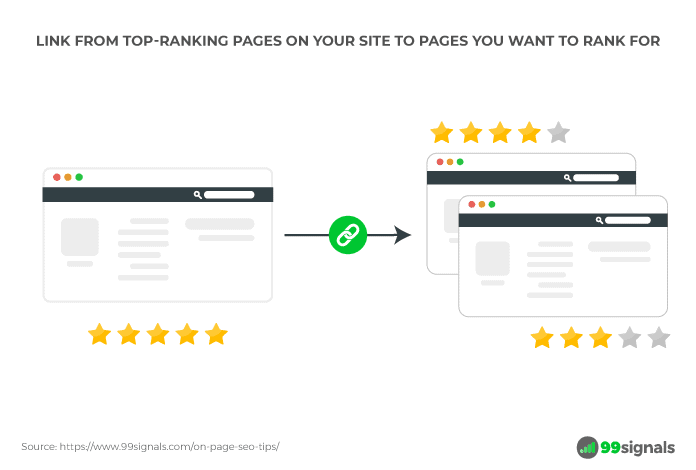

An external link is a hyperlink that points to an external website. There is still much debate on whether external links help boost a site’s SEO. A study by Reboot Online suggests that external linking has a positive impact on search rankings.
Furthermore, top SEOs believe that external links are more influential than internal links.
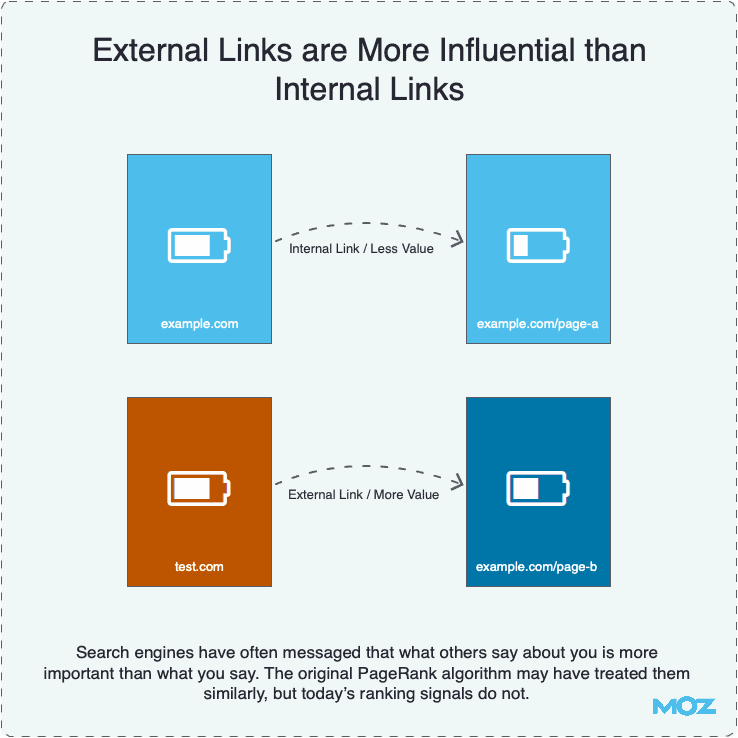

Image Credit: Moz
An SEO best practice would be to link to authoritative websites wherever relevant, using descriptive keywords in anchor text that reflect the same keywords your page is trying to target.
Have you ever given up sharing a shareable piece of content just because you couldn’t find the social sharing buttons? It has happened to me several times. That’s why I recommend using a social bar that follows the content right to the bottom of the page. This allows readers to share the content on your site whenever they’d like.

If you’re using WordPress, I highly recommend you use a social sharing plugin like Social Snap. To learn more about Social Snap, you can watch my in-depth Social Snap video review and walkthrough below:
17. Run a Monthly Site Audit to Fix On-Site Errors
If you really value SEO of your website, you should run a site audit every month in order to identify and fix your on-site errors.
I recommend using Semrush to scan your site for errors. If you don’t have a
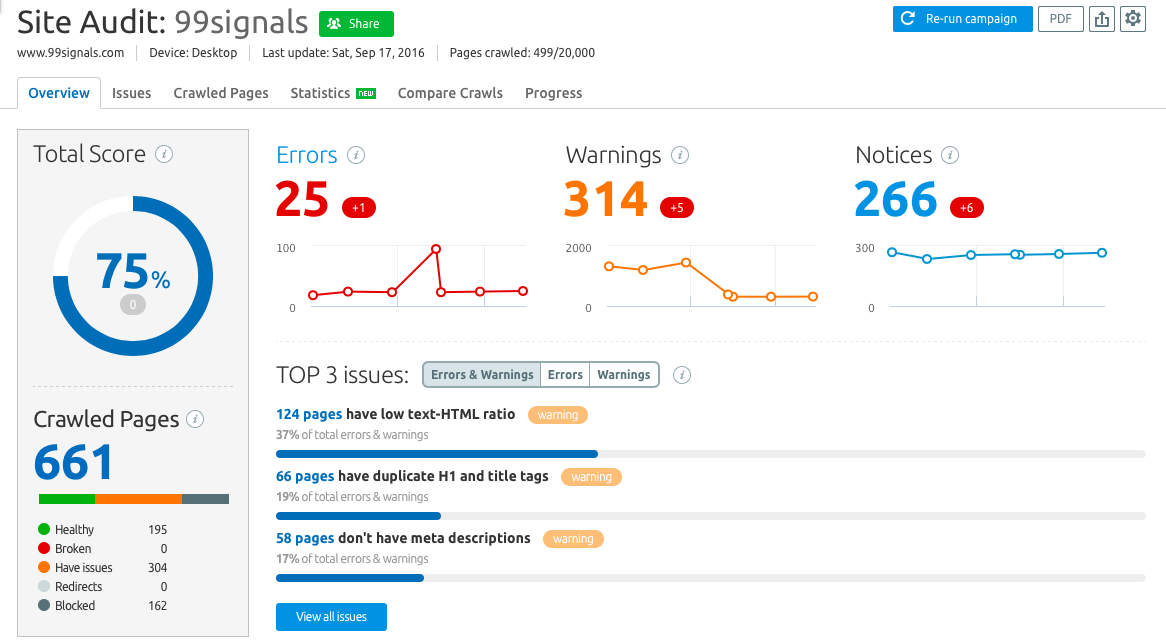

Semrush will not just identify the on-site issues on your site, but also recommend actionable tips to fix them.
18. Use a Number in Your Title Tag
While you may not agree with the editorial standards of publications like Huffington Post, Buzzfeed, and Mashable, one can’t ignore their immense popularity.
Check out these Buzzfeed articles below. Notice anything unique?






Yes, you guessed it! All these posts use numbers in their title tags.
Several industry reports have found that numbers in title tags significantly boost CTR. So whenever possible, include a number in your title tag.
19. Increase “Dwell Time”
If a majority of users click the back button immediately after landing on your site, it’s a sign of a low-quality page and Google is going to penalize you for it. This SEO scenario is called pogo-sticking and it can negatively impact your rankings in the long run.
Google and other search engines use “dwell time” to evaluate a site’s content quality.
One way to increase dwell time is to publish long, informative content that encourages your visitors to stay on the site longer.
Recommended reading: Pogo-Sticking in SEO: 9 Ways to Make Your Content More Engaging
20. Make Your Website 100% Mobile-Friendly
Mobile-friendly websites got a significant boost in search rankings after Google’s search algorithm update in April 2015, aka mobilegeddon. On the other hand, websites that were not mobile-friendly saw their rankings drop in SERPs.
Fast forward to today and it’s more important than ever to have a mobile-friendly website. So make sure every page on your website is mobile-friendly.
Use tools such as Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and HubSpot’s Website Grader to determine the mobile-friendliness of your website.

Both these tools provide great insights into improving the mobile-friendliness of your website.
Once you’ve achieved the perfect score in mobile-friendliness, make sure you follow the latest mobile SEO best practices to maintain an optimized website for mobile devices.
Summary and On-Page SEO Infographic
On-page SEO involves more work than just optimizing your title tag and meta description. You need to make sure your content matches the search intent of your target keywords and constantly monitor your page speed and UX signals to help your pages rank higher in SERPs.
Do you have a favorite on-page SEO technique I may have missed here? Let me know in the comments section.
Below is an infographic that summarizes all the key points in this article.
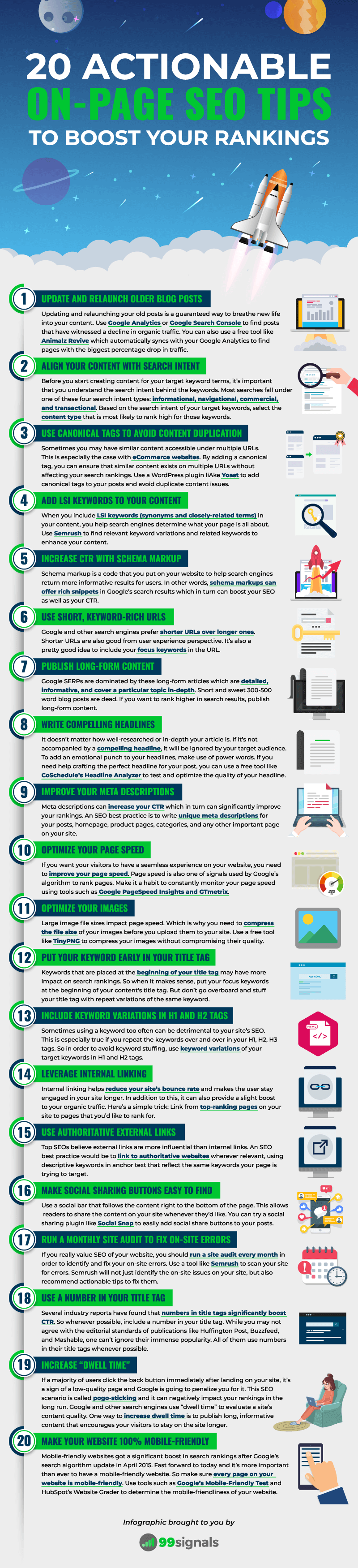

If you found this article useful, please share it on Twitter using the link below:
Editor’s Note: This article was first published on September 28, 2016 and has been updated regularly since then for relevance and comprehensiveness.
Related Articles


